Pipe Belt Conveyor: New type of conveying equipment helps industrial upgrading
Pipe Belt Conveyor
In recent years, with the continuous acceleration of the industrialization process, the demand for logistics and transportation has also increased. While traditional conveying equipment meets the needs of large-scale logistics transportation, there are also some problems, such as large floor space and noise pollution. In order to solve these problems, Pipe Belt Conveyor came into being.
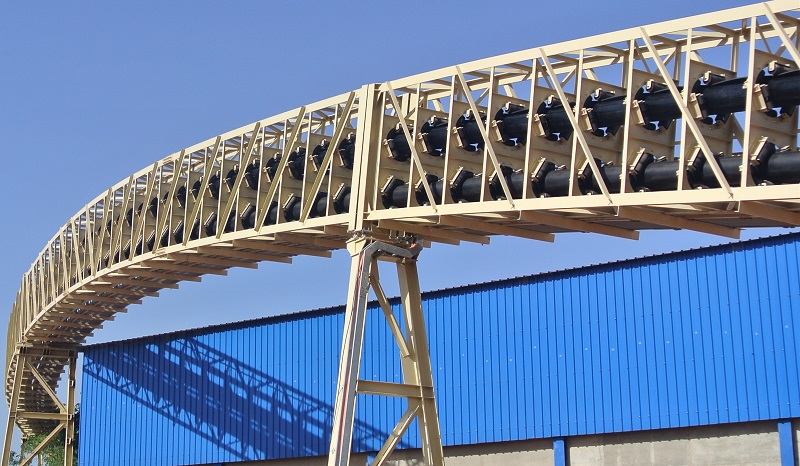

Pipe Belt Conveyor is a new type of conveying equipment, which uses a tubular conveyor belt to wrap the material in the pipe for conveying. Compared with traditional conveying equipment, Pipe Belt Conveyor has the following advantages:
1. Small footprint: Due to the use of tubular conveyor belts, Pipe Belt Conveyor can complete material transportation in a small space, thus saving floor space.
2. Low noise pollution: Traditional conveying equipment will generate a lot of noise during operation, but the Pipe Belt Conveyor uses a tubular conveyor belt, which can effectively reduce noise pollution.
3. Wide range of applications: Pipe Belt Conveyor is suitable for conveying various materials, including materials in different forms such as powder, granular, and block.
4. High conveying efficiency: Pipe Belt Conveyor adopts a tubular conveyor belt, which can wrap materials in the pipe for conveying, thus avoiding the scattering and accumulation of materials and improving the conveying efficiency.
5. Low maintenance cost: The maintenance cost of the Pipe Belt Conveyor is relatively low, because it uses a tubular conveyor belt, which can effectively reduce the wear and tear of the material on the conveying equipment.
Pipe Belt Conveyor has a wide range of applications and can be used in various logistics transportation scenarios, such as mines, ports, chemical plants, etc. In the mine, the Pipe Belt Conveyor can transport the ore from the mine to the processing plant, thereby improving the utilization rate of the ore; in the port, the Pipe Belt Conveyor can transport the goods from the dock to the cargo ship, thereby increasing the throughput of the port; In a chemical plant, the Pipe Belt Conveyor can transport chemical raw materials from the warehouse to the production line, thereby improving production efficiency.
At present, many enterprises at home and abroad have begun to use Pipe Belt Conveyor for logistics transportation, such as ContiTech in Germany and Bridgestone in the United States. In China, some large enterprises have also begun to introduce Pipe Belt Conveyor, such as Baosteel Group and Aluminum Corporation of China.
With the continuous acceleration of the industrialization process, the demand for logistics and transportation will also continue to grow. As a new type of conveying equipment, Pipe Belt Conveyor will play an increasingly important role in the future logistics and transportation field.
 O'zbek
O'zbek slovenský
slovenský Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan Қазақ
Қазақ Latine
Latine ລາວ
ລາວ български
български नेपाली
नेपाली فارسی
فارسی Javanese
Javanese Українська
Українська Lietuvos
Lietuvos Română
Română Slovenski
Slovenski پښتو
پښتو Punjabi
Punjabi Bosanski
Bosanski Malti
Malti Galego
Galego Afrikaans
Afrikaans Esperanto
Esperanto 简体中文
简体中文 Српски
Српски मराठी
मराठी Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά čeština
čeština Polski
Polski ไทย
ไทย Nederlands
Nederlands Italiano
Italiano Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt Deutsch
Deutsch français
français русский
русский Português
Português Español
Español 한국어
한국어 Svenska
Svenska Malay
Malay اردو
اردو norsk
norsk Indonesia
Indonesia عربى
عربى Gaeilge
Gaeilge Türk
Türk Pilipino
Pilipino हिन्दी
हिन्दी Dansk
Dansk বাংলা
বাংলা English
English


What Advantages Do Apron Feeders Offer for High-Temperature Material Handling
In industries such as cement production, metallurgy, power generation, and mineral processing, material handling systems are often exposed to extreme heat. Moving hot clinker, sintered ore, slag, or furnace discharge requires equipment that can tolerate high temperatures without compromising safety or reliability. In these demanding environments, apron feeders have become a preferred solution due to their heat-resistant design and stable operating performance.
Read MoreWhy Are Apron Feeders Preferred for Heavy-Duty and Abrasive Materials
In mining, quarrying, and bulk material handling industries, equipment reliability directly affects productivity and operating costs. When it comes to moving heavy-duty and abrasive materials such as ore, limestone, clinker, and slag, apron feeders are widely preferred over lighter conveying systems. Their continued popularity is driven by practical engineering advantages that match the extreme demands of these applications.
Read MoreWhat Causes Excessive Wear on Conveyor Belt Edges and How to Prevent It
Excessive conveyor belt edge wear—caused by misalignment, uneven loading, worn rollers, or debris—can be minimized through proper alignment, even material distribution, regular maintenance, and protective measures like skirting and edge guards.
Read More